Organic carbon
Maps of soil organic carbon content in different layers and at different scales
Soil organic carbon constitutes about 58% of soil organic matter. The organic matter is composed of a once living organisms as remains of plants and animals in various stages of decomposition, cells or tissues and substances produced or reworked by the roots of plants and microorganisms present in the soil.
In total absence of organic materials, as happens in the sandy desert, there is no soil but only a non- consolidated sediment. It’s therefore clear the importance of soil organic matter: in fact its presence is required to give meaning to the notion of soil.
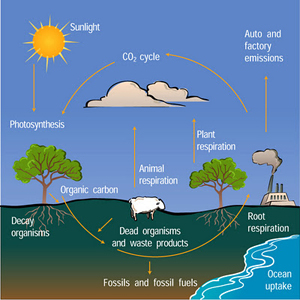
The cycle of the organic matter is extremely complex because formed by a set of various more simple cycles. The most important is the carbon cycle where plants use solar energy and CO2 present in the atmosphere.
These functions are provided by soil organic matter:
source of energy for the soil microorganisms;
it preserves and provides nutrients needed for crop and micro-organisms growth;
it retains the nutrients thanks to its cation and anion exchange capacity;
it stabilizes and holds together the soil particles reducing erosion;
it improves the structure making it more granular and consequently porosity, bulk density and permeability are improved as well, by adjusting the shallow and deep water flows;
it reduces the negative effects of pesticides, heavy metals and many other pollutants on the environment.
The organic matter, acting on soil structure, reduces the formation of crusts on the surface , increases the rate of water infiltration, reduces the superficial flow and facilitates the penetration of plant roots.
The ability to subtract organic carbon from the atmosphere has to be added to these functions. CO2 is fixed by the photosynthetic activity of the plants and, through the plant residues and the root exudates, it is accumulated in the soil in form of more or less humidified organic matter. Hence the recognition of the role of the soil in the carbon cycle by the international conventions on Desertification (Paris, 1994) and on climate change and biodiversity (Rio de Janeiro, 1992).
Soil organic matter performs many and important functions, so its decline is considered a threat and a soil degradation element, as indicated in the Communication from the European Commission "Thematic Strategy for Soil Protection” (COM/2006/0231).
Available Maps
The Geology, Soil and Seismic Risk Area has produced some maps describing the organic carbon content in regional soils in order to orient the management, protection and conservation policies. The following maps are available:
Percentage soil organic carbon content in 0-30 cm and 0-100 cm layer (plain at 1:50k scale, hills and mountain at 1:250k scale). This parameter provides information on the status of soil fertility and influences many physical - chemical properties of soil. It is also a parameter used in simulation models (eg. estimation of the water balance);
Soil organic carbon stock in 0-30 cm layer and 0-100 cm layer (plain at 1:50k scale, hills and mountain at 1:250k scale). This parameter provides information on the amount of organic carbon and thus CO2 currently present in the soils of Emilia-Romagna region, from which we can estimate the storage capacity or potential loss of CO2 as a result of use changes or different agronomic management of soils;
Evaluation of Organic Matter content in 0-30 cm layer. This parameter describes in qualitative terms, using 3 classes, the organic matter content as a function of soil texture. This type of assessment is used in the Guidelines for Integrated production of Emilia-Romagna region (DPI 2023) to guide organic fertilisation in order to improve soil quality and its productive potential while respecting the environment.
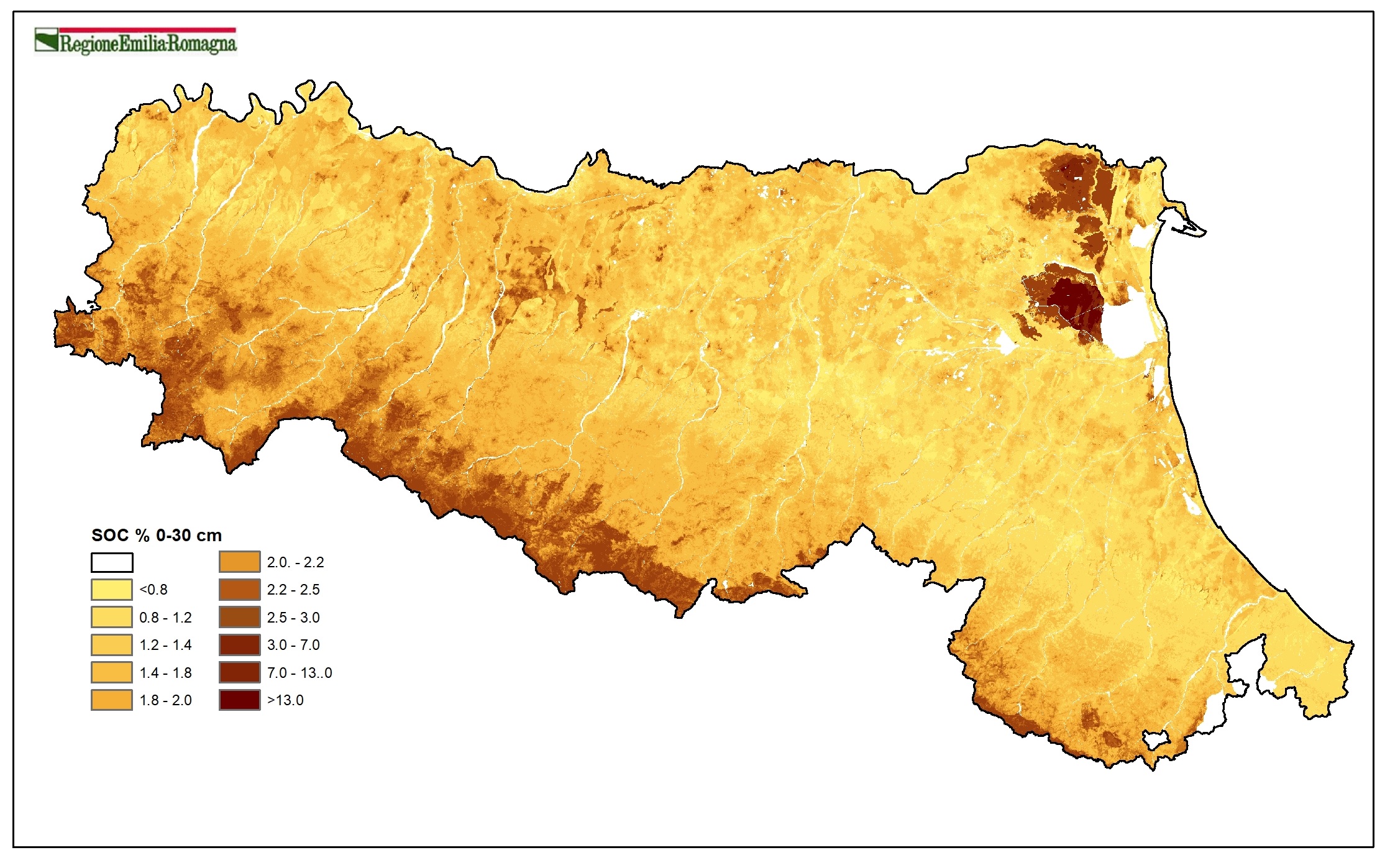
Soil organic carbon %. 0-30 cm (2023). Raster layer (pixel 100mx100m). DOWNLOAD
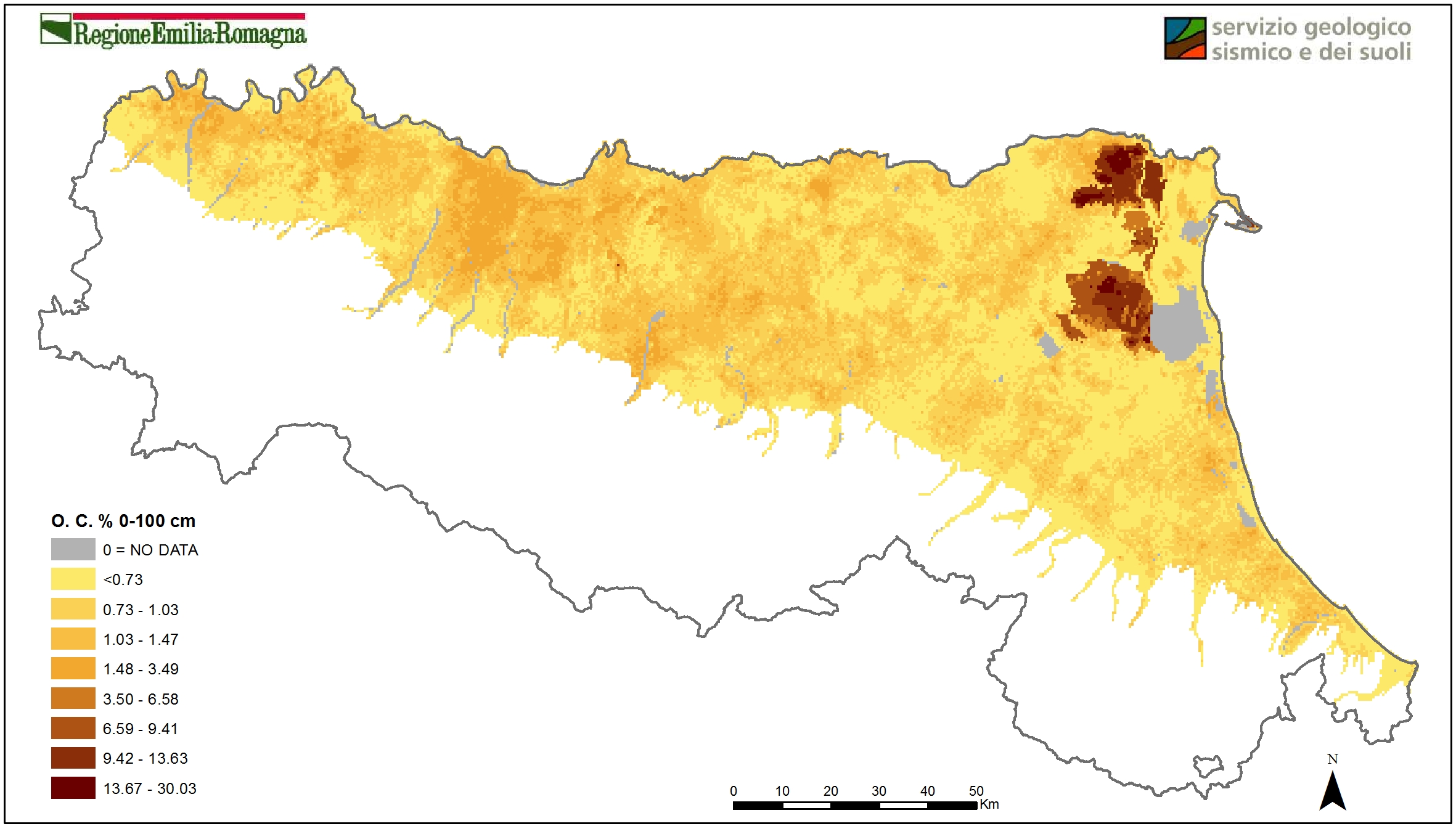
Soil organic carbon % 0-100 cm (2015). Vector layer (tile 500mx500m).
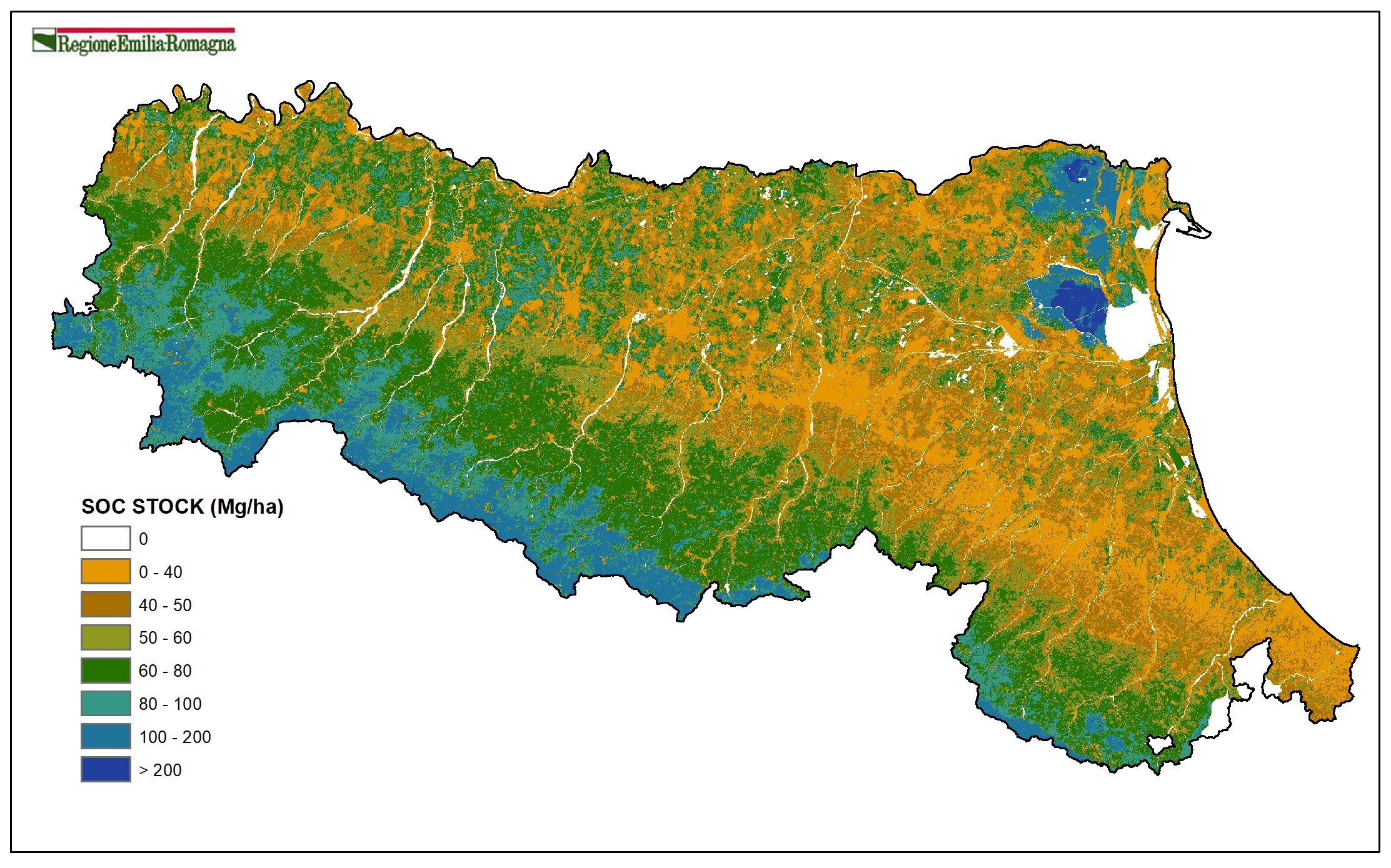
Soil carbon stock (Mg/ha) 0-30 cm (2023). Raster layer (pixel 100mx100m). DOWNLOAD
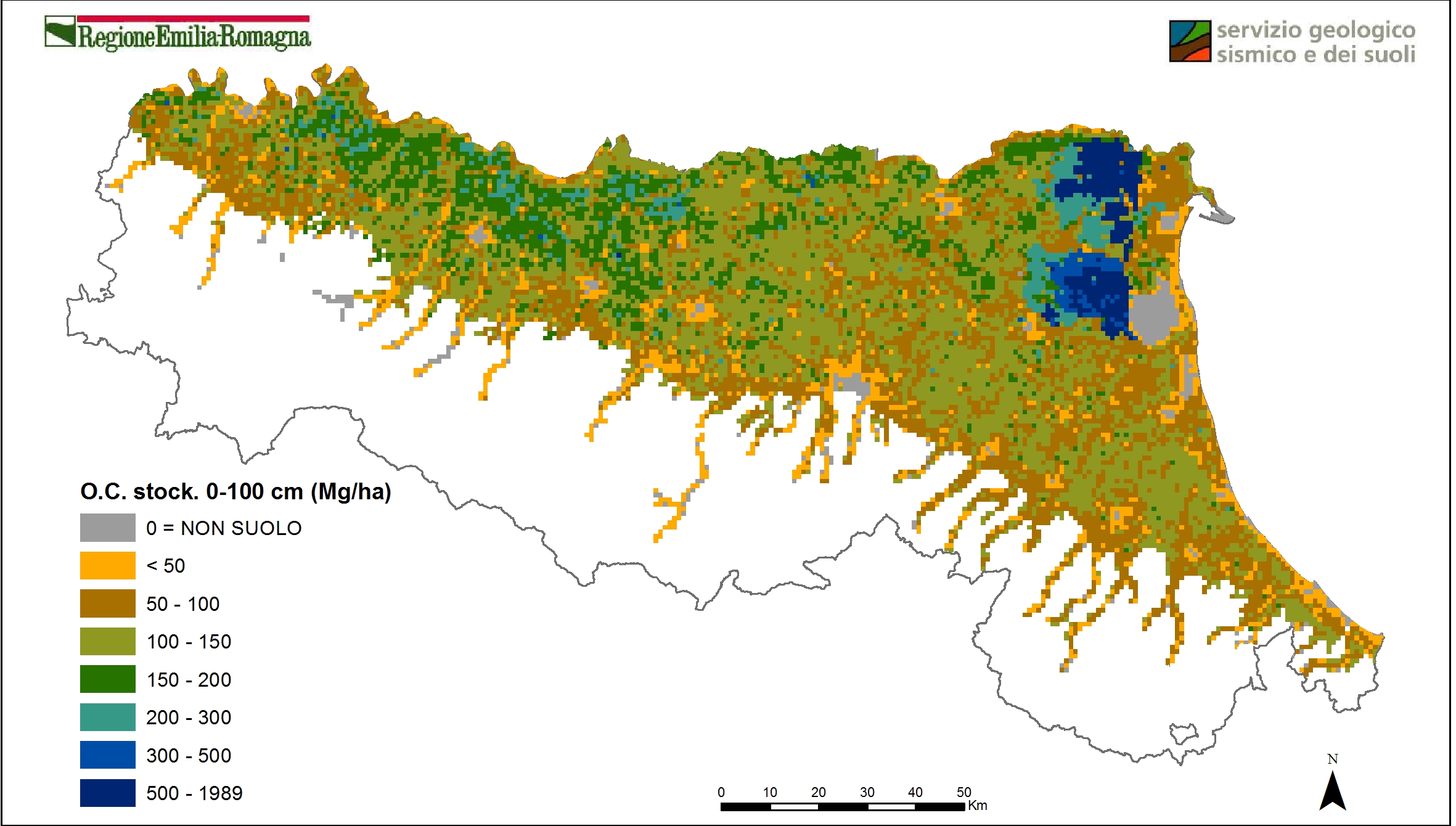
Soil carbon stock (Mg/ha). 0-100 cm (2010). Vector layer (tile 1kmx1km). DOWNLOAD
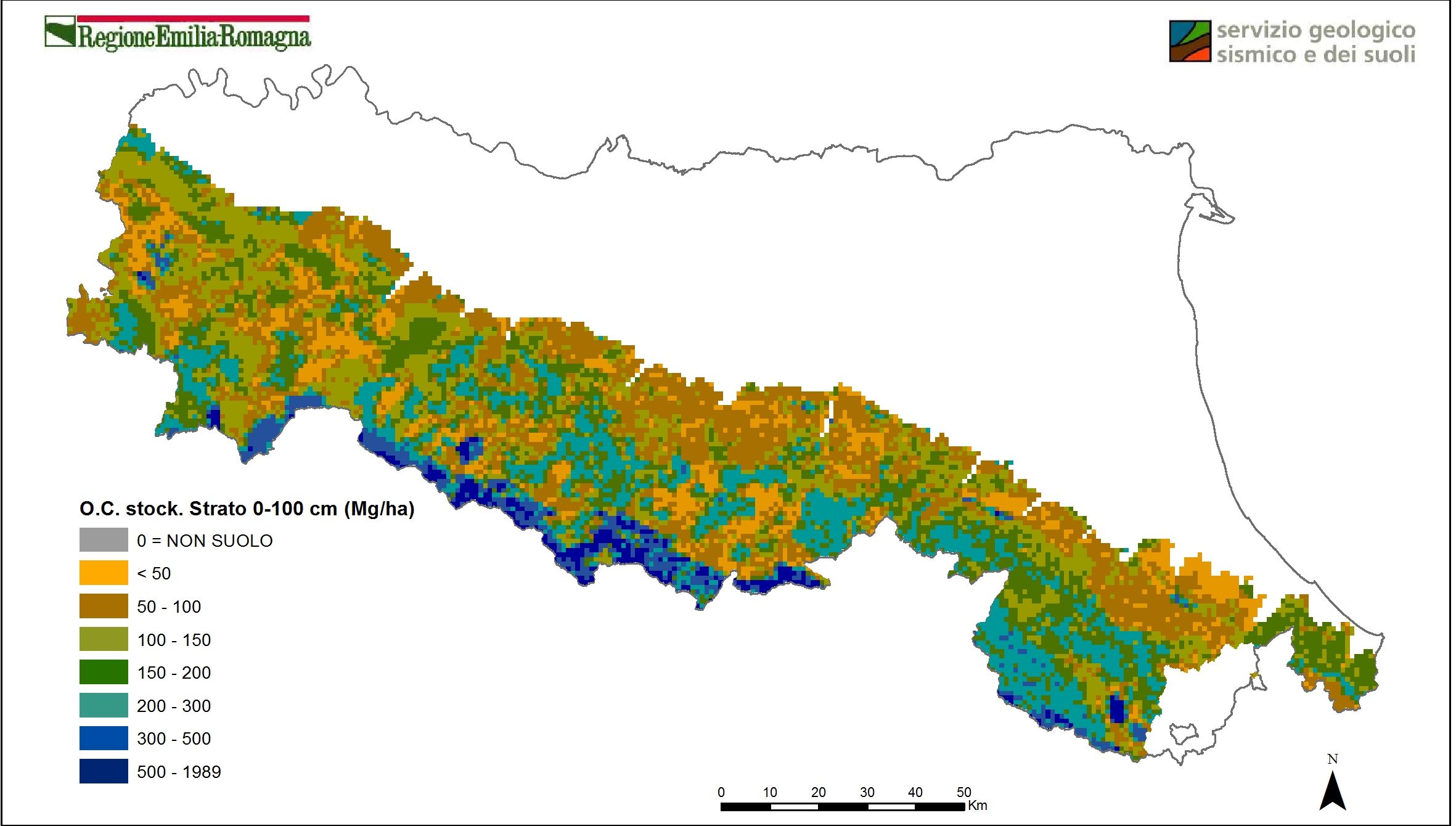
Soil carbon stock (Mg/ha). 0-100 cm (2010). Vector layer (tile 1kmx1km). DOWNLOAD

Evaluation of Organic Matter content. 0-30 cm (2023). Raster layer (pixel 100mx100m). DOWNLOAD
Web mapping
- Soil Catalog of Emilia-Romagna
The website provides access to 1:50k soil map and point data (extension service soil analyses and shallow water table measurement sites). A selection of derived thematic maps is available as well. It’s possible to draw plots, to identify a soil type using a tool and to calculate the fertilisation plans. It is especially aimed at users in the agricoltural sector. - Soil maps of Emilia-Romagna
- Soils of Emilia-Romagna
- Minerva Portal
It's possible to query and download metadata and data in open data format (shapefiles, TIFF, WMS, CSV and TXT tables).
It is a webgis site that contains all published maps (soils maps and derived maps), as well as some point layers (Extension Service soil analyses, heavy metal analyses, shallow groundwater network stations). It allows simultaneous consultation of multiple layers. Many aerial flight/satellite images from 1944 to 2023 are available. It is especially aimed at users in the environmental and educational sectors.
It is an easy-to-use site that describes the main features of the region's soils and landscapes. Through Google Earth, it makes available the cartography of Emilia-Romagna soils at different scales (from scale 1:1,000,000 up to maps of farm soils). In the "Thematic Maps" section, it is also possible to consult application maps (e.g., use capacity, natural anthropic background of heavy metals) and maps of the chemical-physical properties of soils (e.g., organic C content, natural background of heavy metals, texture, pH, salinity).