Salinity
Soil salinity is the soluble salt content in the soil, mainly chlorides (Cl-), sulphates (SO42-),bicarbonates (HCO3-) and different types of carbonates (CO32-): calcium (Ca2+), magnesium (Mg2+), sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+). The problem of soil salinisation (the process of increasing the salt content) is considered a threat and a soil degradation element in the Communication from the European Commission "Thematic Strategy for Soil Protection” (COM/2006/0231). In this document soil salinisation has been proposed as a research field: “Further research is necessary to close the gaps in knowledge about soil and strengthen the foundation for policies”.
Following these indications and in accordance with the Regional Agricultural Extension Service salinity maps of the soils of Emilia-Romagna plain at 1:250,000 scale (first/second edition) have been prepared.

(photo by Raimondi)
Soil salinity maps describe the status of salinity in topsoil (layer 0-50 cm) and subsoil (layer 50-100 cm), using the electrical conductivity of saturated paste extract at 25°C (dS/m). ECe values are classified according to Soil Survey Manual (1993).
These maps are a first regional-scale spatial representation derived by geo-statistical analysis on point data collected in different soil surveys.
Available maps
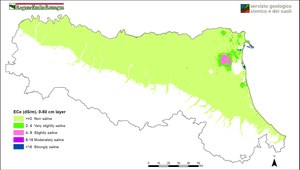
Electrical conductivity ECe(dS/m), layer 0-50 - Enlarge image (548.16 KB)
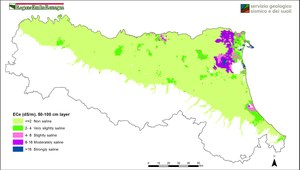
Electrical conductivity ECe(dS/m), layer 50-100 - Enlarge image (589.5 KB)
Contact us
Geological, Soil and Seismic Risk Area
e-mail - phone +39 051 5274792
